Unpacking the “black box” to build better AI models

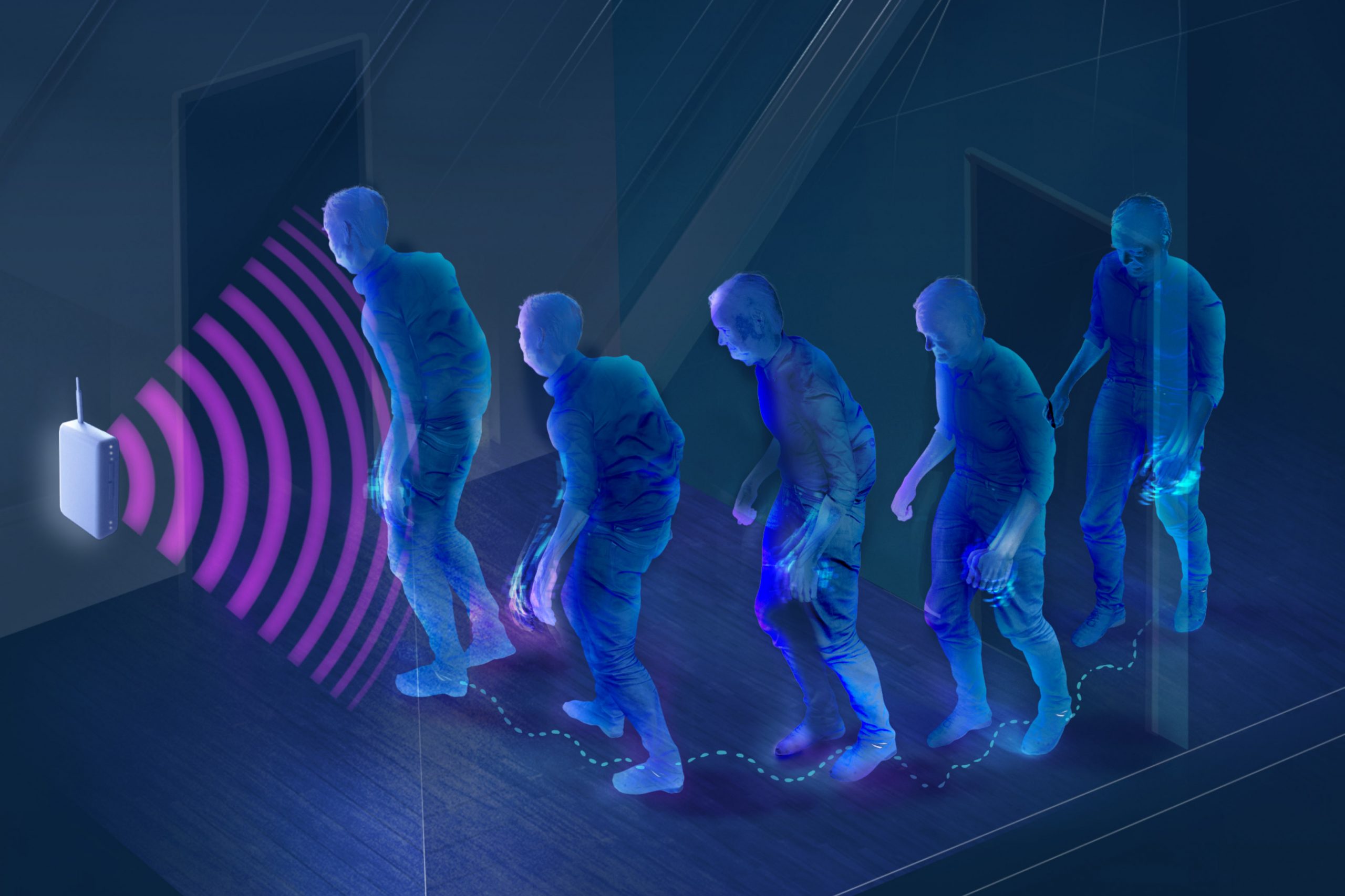
When deep learning models are deployed in the real world, perhaps to detect financial fraud from credit card activity or identify cancer in medical images, they are often able to outperform humans.
But what exactly are these deep learning models …